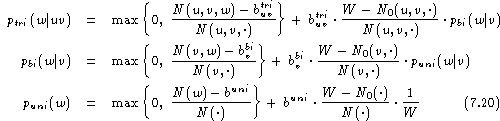
To illustrate all the details involved in smoothing a trigram model, we will write down the full set of equations that is needed to smooth a trigram language model. Any of the three smoothing methods can be used for this purpose. Here, we will consider only absolute discounting in connection with interpolation . At the levels of bigrams and unigrams , we have to apply the same operation. Without using the singleton distribution, we obtain the full trigram model:
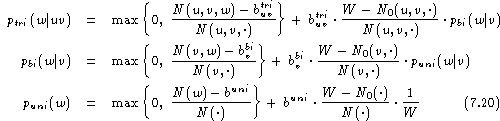
The advantage of interpolation in comparison
with backing-off is that
the computationally costly renormalisation is avoided;
the experiments show that the perplexities are virtually not affected.
The smoothing at the level of unigrams will be required
only in exceptional cases when the size of the training
corpus is extremely small. In all other conditions,
we will set: ![]() .
.
Note that we have not used the singleton distribution. In this case, the normal bigram model has to be replaced by the corresponding singleton counts, that is
![]()
When using the singleton distribution, we have to be careful in using the leaving-one-out concept because the set of events now is not any more the full set of training data but only the corresponding singleton subset. As to the choice of history dependent versus history independent discounting parameters, it is important to know that the experimental tests show that the history dependence does not pay off, at least for absolute discounting. So it is sufficient to have only two (!) discounting parameters, namely one for the bigram model and another one for the trigram model.