where
Every approach to automatic speech recognition is faced with the problem of taking decisions in the presence of ambiguity and context, and of modelling the interdependence of these decisions at various levels. If it were possible to recognise phonemes (or words) with a very high reliability, it would not be necessary to rely heavily on delayed decision techniques, error correcting techniques and statistical methods. In the near future, this problem of reliable and virtually error free phoneme or word recognition without using high-level knowledge is unlikely to be solved for large-vocabulary continuous-speech recognition. As a consequence, the recognition system has to deal with a large number of hypotheses about phonemes , words and sentences, and ideally has to take into account the ``high-level constraints'' as given by syntax , semantics and pragmatics . Given this state of affairs, statistical decision theory tells us how to minimise the probability of recognition errors [Bahl et al. (1983)].
The word sequence ![]() to be recognised from the sequence of
acoustic observations
to be recognised from the sequence of
acoustic observations ![]() is determined as that word sequence
is determined as that word sequence
![]() for which the posterior probability
for which the posterior probability
![]() attains its maximum.
The sequence of acoustic vectors
attains its maximum.
The sequence of acoustic vectors
![]() over time t=1...T
is derived from the speech signal in the
preprocessing step of acoustic analysis.
Statistical decision theory leads to the so-called
Bayes decision rule, which can be written in the form:
over time t=1...T
is derived from the speech signal in the
preprocessing step of acoustic analysis.
Statistical decision theory leads to the so-called
Bayes decision rule, which can be written in the form:
![]()
where ![]() is the conditional probability,
given the word sequence
is the conditional probability,
given the word sequence
![]() ,
of observing the sequence of acoustic vectors
,
of observing the sequence of acoustic vectors ![]() and
where
and
where ![]() is the prior probability of producing the word
sequence
is the prior probability of producing the word
sequence ![]() .
The application of the Bayes decision rule
to the speech recognition problem is illustrated in
Figure 7.1.
.
The application of the Bayes decision rule
to the speech recognition problem is illustrated in
Figure 7.1.
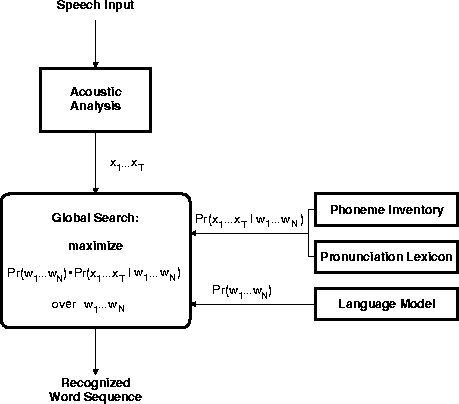
Figure 7.1: Bayes decision rule for speech recognition
The decision rule requires two types of probability distribution, which we refer to as stochastic knowledge sources, along with a search strategy: