




Next: SQL
Up: Data model
Previous: Network data model
The relational model is a data model with a thorough mathematical foundation.
An attribute is a named set of atomic values, the domain. A
relation
table is a subset of the cross-product of the relation attributes.
The relational data model separates the logical data definition from physical
storage.
Two data manipulation languages have been developed for the relational data
model:
- Relational algebra is a procedural language which consists of
the set operators
union, intersection, difference and the relational operators selection,
projection,
and join.
The selection operator selects rows from a relation table that meet a selection
condition. The projection operator selects specific attributes from a relation
table. The join operator merges relation tables according to a
comparison condition over attributes from the original relation tables.
The result of a relational operation is again a relation, so that
the operators can be nested.
- Relational calculus is a declarative language based on
first-order predicate
logic.
An expression is a term of the form
with 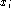 variables over a domain and COND a formula that is either true
or false.
The variable bindings on the left side of the vertical bar are the values
returned
as the result of a query, and COND consists of atomic formulas which are
connected
through logical AND and OR operators.
variables over a domain and COND a formula that is either true
or false.
The variable bindings on the left side of the vertical bar are the values
returned
as the result of a query, and COND consists of atomic formulas which are
connected
through logical AND and OR operators.
The relational data model makes no assumptions about the relationships between
entities. In general, an entity is mapped to a relation table, with the
properties
of an entity described through the relation attributes. Meaningful relationships
between entities are expressed through relational algebra operations or
calculus
expressions. Hence, complex relationships between entities can be
expressed, with
the notable expression of recursive relationships.
EAGLES SWLG SoftEdition, May 1997. Get the book...
![]() variables over a domain and COND a formula that is either true
or false.
The variable bindings on the left side of the vertical bar are the values
returned
as the result of a query, and COND consists of atomic formulas which are
connected
through logical AND and OR operators.
variables over a domain and COND a formula that is either true
or false.
The variable bindings on the left side of the vertical bar are the values
returned
as the result of a query, and COND consists of atomic formulas which are
connected
through logical AND and OR operators.