




Next: Comparative and indirect assessment
Up: Scoring procedures
Previous: Open-set identification
These recommendations indicate how the performance of a speaker
recognition system should be scored.
-
For closed-set identification
- -
-
Beside the test set misclassification rate
(
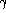 ), report on average misclassification and mistrust
rates (
), report on average misclassification and mistrust
rates (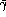 and
and 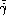 ), and provide also
gender-balanced rates (
), and provide also
gender-balanced rates (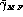 and
and
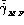 ) if the test population is
composed of male and female speakers.
) if the test population is
composed of male and female speakers.
- -
-
As the number of registered speakers is a crucial factor of performance, it is essential to indicate the number of speakers in the registered speaker population. Mention also the proportion of male and female speakers for information.
- -
-
For statistical validity information, indicate the number and male/female proportion of speakers in the test population and the average number of test utterances per test speaker.
-
For verification
- -
-
For static evaluation, beside the test set false rejection
rate (
 ) and the test set false
acceptance rate (
) and the test set false
acceptance rate (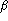 ), provide the average false rejection rate (
), provide the average false rejection rate ( ) and the average false acceptance rate (
) and the average false acceptance rate (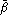 or
or 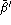 depending on whether the impostors' identities are known or not). Gender-balanced rates (
depending on whether the impostors' identities are known or not). Gender-balanced rates (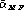 and
and 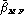 or
or 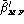 ) should also be reported.
) should also be reported.
- -
-
For dynamic evaluation and a speaker-independent threshold,
the system ROC curve should be obtained as:
-
either
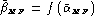 (or
(or 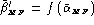 if impostors are unknown),
if impostors are unknown),
-
or
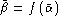 (or
(or 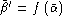 if impostors are unknown),
if impostors are unknown),
-
or
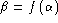
Summarise a ROC curve by its traditional equal error rate (respectively 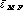 ,
,  and
and  ). Investigate on the possibility of finding a ROC curve model, and report the model equal error rate (
). Investigate on the possibility of finding a ROC curve model, and report the model equal error rate (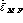 ,
, 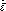 and
and  ) and the
) and the 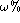 -accuracy false rejection rate validity domain
-accuracy false rejection rate validity domain 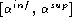 . Find a reasonable compromise between
. Find a reasonable compromise between  and
and 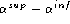 .
.
- -
-
For dynamic evaluation with speaker-dependent thresholds , compute the
individual equal error rate (
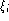 ) of each ROC curve
) of each ROC curve 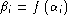 and give the gender-balanced equal error
rate
(
and give the gender-balanced equal error
rate
(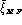 ), the average equal error rate
(
), the average equal error rate
(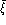 ) and the test set equal error rate (
) and the test set equal error rate (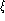 ). Investigate the
possibility of fitting a common ROC curve model by adjusting individually a
model equal error rate (
). Investigate the
possibility of fitting a common ROC curve model by adjusting individually a
model equal error rate (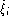 ) for each curve. Here, either an
accuracy
) for each curve. Here, either an
accuracy  is fixed and speaker-dependent validity domains are
computed, or the validity domain is fixed in a speaker-independent
manner
and the individual accuracy
is fixed and speaker-dependent validity domains are
computed, or the validity domain is fixed in a speaker-independent
manner
and the individual accuracy 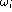 is computed. Compute anyway the
global model equal error rates (
is computed. Compute anyway the
global model equal error rates (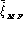 ,
,
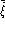 and
and 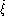 ). Then give accordingly either the average
validity domain for a speaker-independent
accuracy or the average accuracy
for a speaker-independent validity domain.
). Then give accordingly either the average
validity domain for a speaker-independent
accuracy or the average accuracy
for a speaker-independent validity domain.
- -
-
For statistical validity information, indicate the number of registered
speakers , the proportion of male and female
registered speakers , the number of genuine test
speakers , the proportion of male and female genuine
test speakers and the average number of genuine test utterances per genuine
test speaker. Give also a relevant description of the test impostor
configuration and population.
-
For open-set identification
- -
-
For static evaluation, score separately the false rejections (
 ,
,  and
and 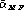 ), the false acceptances (
), the false acceptances (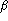 ,
, 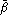 or
or 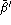 and
and 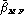 or
or 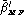 ) and the misclassifications (
) and the misclassifications (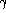 ,
, 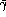 and
and 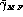 ).
).
- -
-
For dynamic evaluation and a speaker-independent threshold, project the
three-dimensional ROC curve
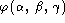 into two curves
into two curves
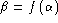 and
and 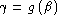 . Summarise the first one as
its equal error rate
. Summarise the first one as
its equal error rate  and the
second one as its extremity
and the
second one as its extremity 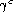 . Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
. Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
- -
-
For dynamic evaluation with speaker-dependent thresholds , average individual
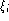 and individual
and individual 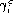 . Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
. Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
- -
-
As for closed-set identification and for
verification, give all relevant information concerning the registered
population, the genuine test population and the impostor population and test
configuration.
In practice, gender-balanced average and test
set scores are obtained very easily as various linear combinations of
individual speaker scores.





Next: Comparative and indirect assessment
Up: Scoring procedures
Previous: Open-set identification
EAGLES SWLG SoftEdition, May 1997. Get the book...
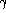 ), report on average misclassification and mistrust
rates (
), report on average misclassification and mistrust
rates (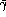 and
and 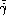 ), and provide also
gender-balanced rates (
), and provide also
gender-balanced rates (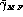 and
and
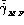 ) if the test population is
composed of male and female speakers.
) if the test population is
composed of male and female speakers.
 ) and the test set false
acceptance rate (
) and the test set false
acceptance rate (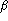 ), provide the average false rejection rate (
), provide the average false rejection rate ( ) and the average false acceptance rate (
) and the average false acceptance rate (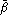 or
or 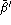 depending on whether the impostors' identities are known or not). Gender-balanced rates (
depending on whether the impostors' identities are known or not). Gender-balanced rates (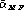 and
and 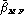 or
or 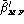 ) should also be reported.
) should also be reported.
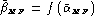 (or
(or 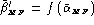 if impostors are unknown),
if impostors are unknown),
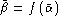 (or
(or 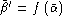 if impostors are unknown),
if impostors are unknown),
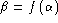
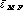 ,
,  and
and  ). Investigate on the possibility of finding a ROC curve model, and report the model equal error rate (
). Investigate on the possibility of finding a ROC curve model, and report the model equal error rate (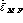 ,
, 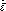 and
and  ) and the
) and the 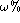 -accuracy false rejection rate validity domain
-accuracy false rejection rate validity domain 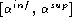 . Find a reasonable compromise between
. Find a reasonable compromise between  and
and 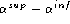 .
.
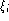 ) of each ROC curve
) of each ROC curve 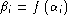 and give the gender-balanced equal error
rate
(
and give the gender-balanced equal error
rate
(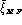 ), the average equal error rate
(
), the average equal error rate
(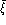 ) and the test set equal error rate (
) and the test set equal error rate (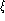 ). Investigate the
possibility of fitting a common ROC curve model by adjusting individually a
model equal error rate (
). Investigate the
possibility of fitting a common ROC curve model by adjusting individually a
model equal error rate (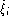 ) for each curve. Here, either an
accuracy
) for each curve. Here, either an
accuracy  is fixed and speaker-dependent validity domains are
computed, or the validity domain is fixed in a speaker-independent
manner
and the individual accuracy
is fixed and speaker-dependent validity domains are
computed, or the validity domain is fixed in a speaker-independent
manner
and the individual accuracy 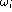 is computed. Compute anyway the
global model equal error rates (
is computed. Compute anyway the
global model equal error rates (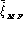 ,
,
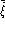 and
and 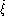 ). Then give accordingly either the average
validity domain for a speaker-independent
accuracy or the average accuracy
for a speaker-independent validity domain.
). Then give accordingly either the average
validity domain for a speaker-independent
accuracy or the average accuracy
for a speaker-independent validity domain.
 ,
,  and
and 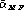 ), the false acceptances (
), the false acceptances (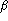 ,
, 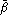 or
or 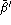 and
and 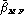 or
or 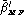 ) and the misclassifications (
) and the misclassifications (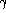 ,
, 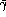 and
and 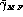 ).
).
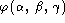 into two curves
into two curves
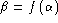 and
and 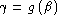 . Summarise the first one as
its equal error rate
. Summarise the first one as
its equal error rate  and the
second one as its extremity
and the
second one as its extremity 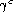 . Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
. Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
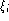 and individual
and individual 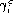 . Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.
. Investigate the possibility of
using a parametric approach.